- The most in-demand skills in 2026 combine technical and human capabilities: AI, data, cybersecurity, cloud, and green technologies are rising fastest, alongside leadership, emotional intelligence, adaptability, and judgment.
- Routine and repetitive skills are declining due to automation: Data entry, basic accounting, telemarketing, customer service, and administrative support skills are shrinking as AI and automation take over standardized tasks.
- Organizations must shift to skills-based workforce strategies: Tracking skills in real time, investing in continuous upskilling, and aligning learning with business outcomes are critical to staying competitive in an AI-driven economy.
By 2026, AI, automation, and global shifts will shape the most in-demand. To keep up, leaders must know:
- Which skills are growing fastest
- Which skills are declining
- How to develop their teams’ capabilities
Why workforce skills matter more than ever
The workplace is changing faster than ever. Through 2025, the skills we value most changed massively. Technical capabilities, like AI engineering and data science, became more in demand, while skills like Microsoft Office and data entry fell off. We saw five main factors driving these changes:
1 - Shrinking labor supply – Aging populations, fewer entry-level roles, and global demographic shifts reduced available talent. By 2060, working-age populations are projected to fall 30% in over a quarter of OECD countries (OECD, 2025) Organizations must develop and retain skilled employees to prevent gaps.
2 - Need for unique human value – AI and automation can handle routine tasks, but human judgment, creativity, and leadership remain essential. These uniquely human skills create competitive advantages that machines cannot replicate.
3 - Increase in human connectivity – Hybrid and remote work makes clear communication, collaboration, and emotional intelligence crucial to connect teams and get work done. Teams with strong soft skills are more productive, adaptable, and able to innovate.
4 - Widening skill gaps – Organizations that lacked the right skills lost productivity and fell behind competitors. $11.5 trillion in global productivity is lost annually due to skills gaps. (EY, 2022) Closing skill gaps directly improves efficiency, innovation, and business outcomes.
5 - Skills enable adaptability – Roles and tasks evolve quickly. Employees with the right technical and human skills can adjust to new tools, systems, and challenges. Adaptable workforces are resilient to disruption and ready for future opportunities.
In 2026, AI, automation, and digital tools will transform tasks once done solely by humans. Skills are no longer just a factor of workforce planning. They have become the foundation of organization’s competitive advantage. Success in 2026 will depend on employees combining technical skills with creativity, problem-solving, adaptability, and emotional intelligence. Organizations that invest in identifying, building, and deploying the right skills will be better positioned to thrive in 2026 and beyond.
Technical skills will continue to rise in 2026
Technical skills are the practical abilities needed to perform specific tasks or use tools and systems effectively. They can range from entry-level software knowledge and spreadsheet use to higher-level coding and data analysis skills.
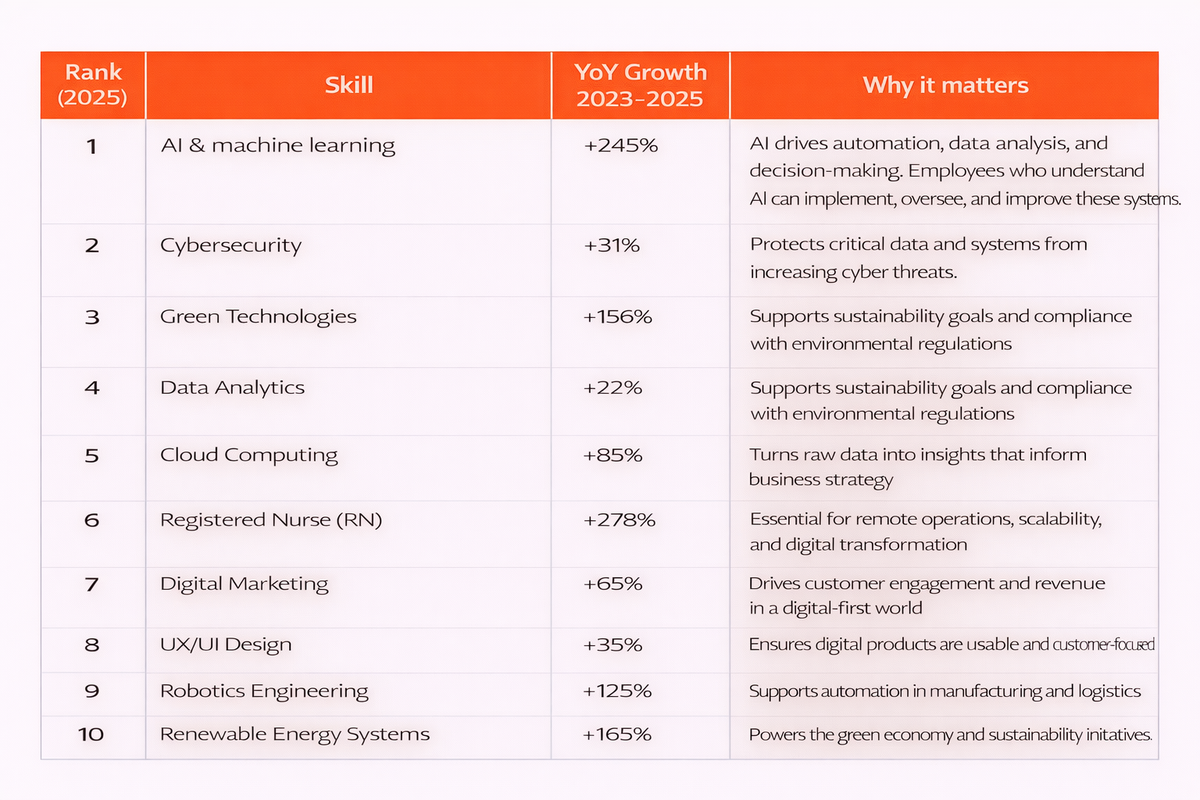
Industry and capability data are proprietary information belonging to Cornerstone; see report for more details.
Why these technical skills are in demand
- They support automation, AI adoption, and digital transformation
- They meet growing global demands in healthcare, sustainability, and digital business
- They enhance organizational agility, enabling faster adaptation to change
The human skills rising in 2026
Human skills are the abilities we use to connect, communicate, and collaborate with others. These include empathy, judgment, creativity, and emotional intelligence, skills that technology cannot replace, and that make people effective in teamwork, leadership, and building relationships.

Industry and capability data are proprietary information belonging to Cornerstone; see report for more details.
Why these human skills are in demand
- Machines cannot replicate empathy, judgment, or leadership
- Organizations are creating hybrid roles requiring both technical and human capabilities
- High-performing teams need skills that drive adaptability, creativity, and collaboration
The 5 skills in decline in 2026
Organizations are questing some skills less often because automation and AI can now handle these routine tasks. Others are becoming standard prerequisites, so they appear less in job postings even though they remain important.
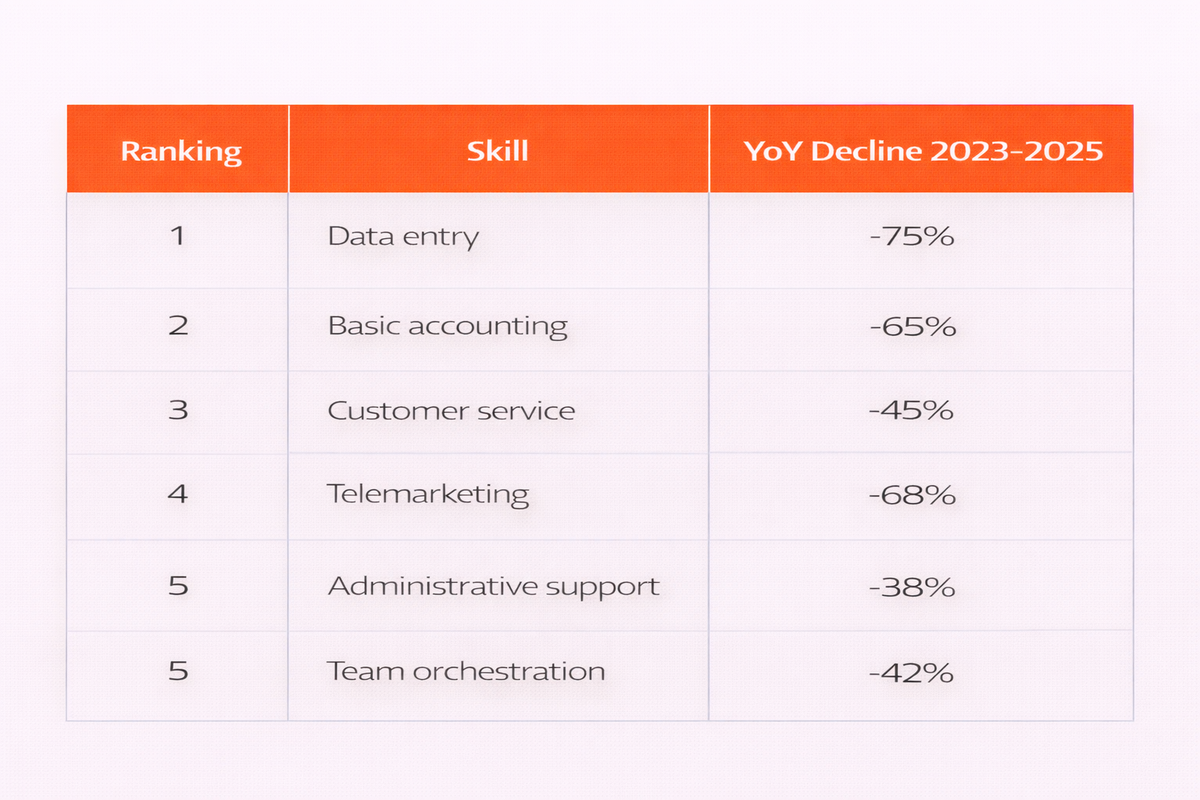
Industry and capability data are proprietary information belonging to Cornerstone; see report for more details.
Key takeaway:
For organizations to maximize the skills they’re focusing on for 2026, they need to invest in skills that complement technology rather than compete with it.
Building both human and technical skills in your workforce
How leaders can build a resilient organization
Step 1: Track workforce skills – Identify current skills and detect gaps early, just like you would with research and development
Step 2: Invest in people’s growth – Treat skills as valuable assets and dedicate resources to developing them
Step 3: Use AI to support learning – Leverage AI tools to enhance work, guide employee development, and boost productivity
Step 4: Measure skill impact – Track improvements in skills, adaptability, and team renewal, not just output
How educators, L&D, and talent teams can close skills gaps
Step 1: Use data to predict skill needs – Identify emerging skills early and start training proactively
Step 2: Build integrated learning programs – Combine technical skills with human skills for a well-rounded workforce
Step 3: Teach holistic skill sets – Include AI, sustainability, and data skills alongside critical thinking, leadership, and empathy
Step 4: Make learning hands-on – Enable employees to apply skills through real projects, simulations, or practical exercises
Step 5: Partner with employers for experience – Offer apprenticeships, internships, and project-based learning to build real-world capabilities
How workers can adapt and thrive
Step 1: Learn and apply AI tools – Make work easier, improve decision-making, and adapt quickly to change
Step 2: Focus on human-centric skills – Develop problem-solving, judgment, and influencing abilities that machines cannot replicate
Step 3: Track and update your skills – Treat your skill set like an investment portfolio and align with emerging trends
Step 4: Take new experiences – Engage in projects, new roles, and certifications to grow your experience and demonstrate adaptability
For a deeper dive into the global skills economy and a full list of top 50 in-demand skills, download the 2026 Cornerstone Skills Economy Report.


