Key Takeaways
- 59% of the skills cited in UAE job postings were human skills compared to 41% percent technical skills
- UAE employers value workers who understand customers, can manage data, and who have strong character
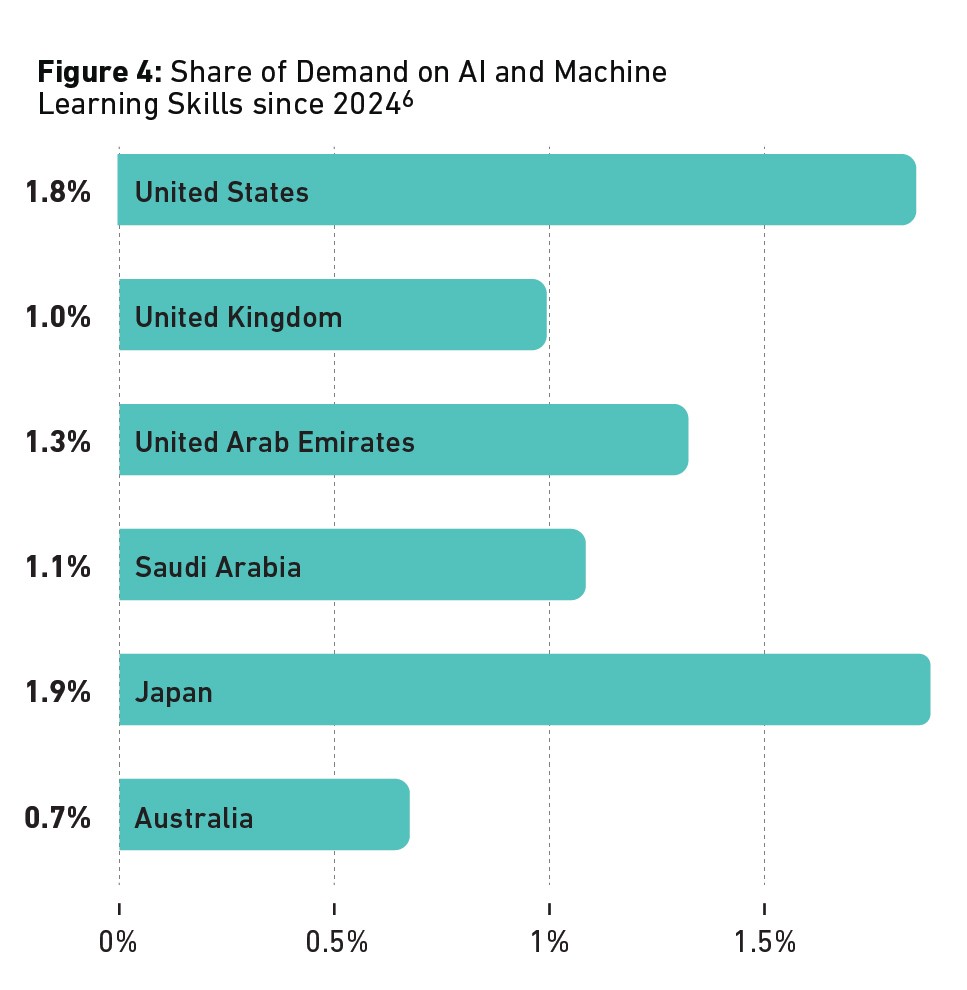
- UAE shows more demand for AI and machine learning skills than the UK, Saudi Arabia, or Australia, but less than the United States
Demand for AI skills is surging in the United Arab Emirates, but UAE employers are still far more likely to ask for human skills than technical ones, according to a new report by the Abdulla Al Ghurair Foundation in partnership with SkyHive by Cornerstone.
In 2024, 59% of the skills cited in UAE job postings were human skills compared to 41% percent technical skills, the report found. Some of the most-requested human skills include communication, management, being a team player, and accountability.
SkyHive has more than 28 terrabytes of labor market data covering more than 200 countries and territories worldwide. Because the data is collected from job postings and CVs posted online, the database is both wide and deep, allowing for both global analysis (as in last year’s Global Skills Economy report) and national deep dives in countries like the UAE.
This kind of insight is vital as skills change rapidly. The World Economic Forum estimates that nearly 4 in 10 (39%) of core job skills will change within five years. If countries are not to be left behind, they need to adjust to these changes.
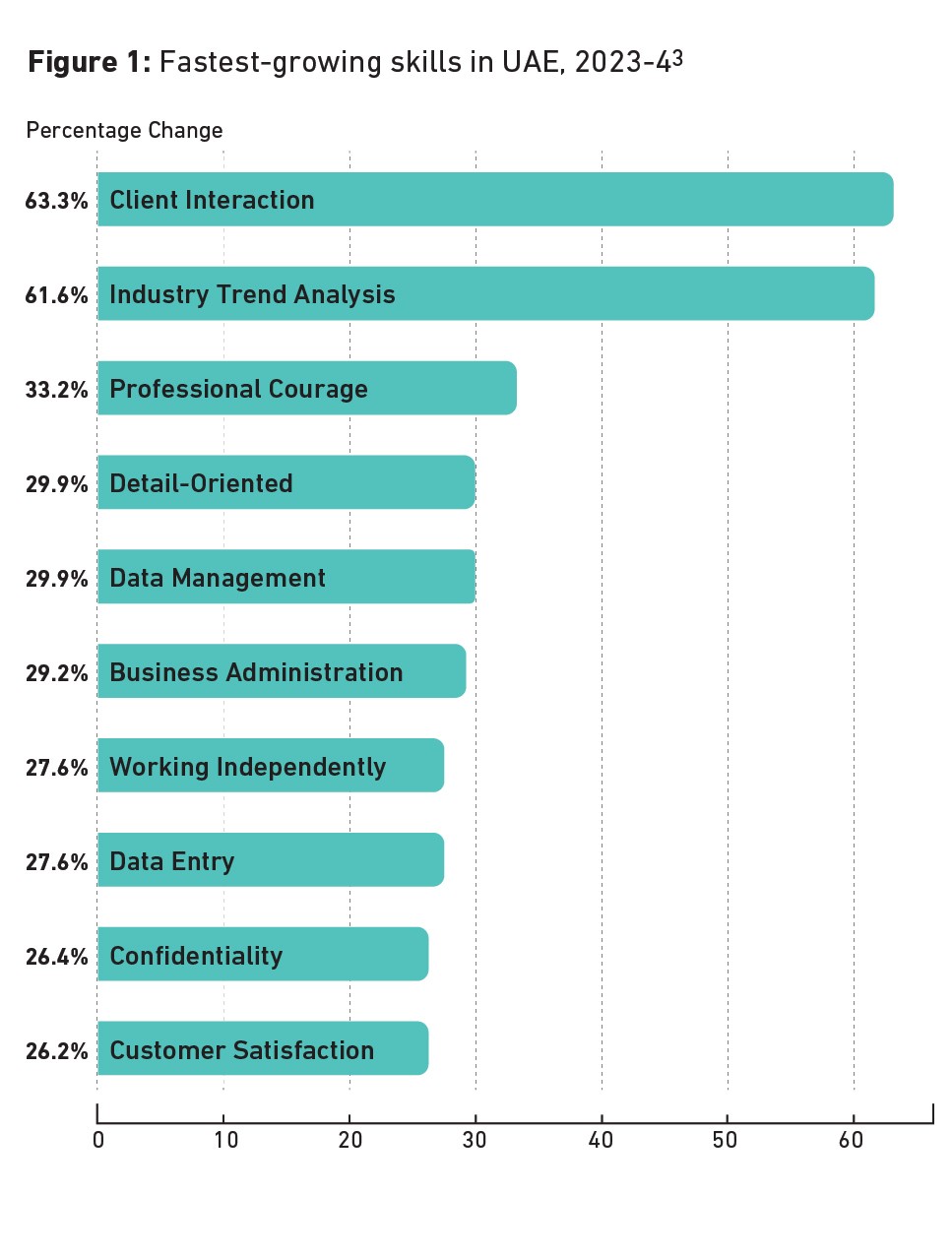
The fastest-growing skills in the UAE
One of the best ways to see whether employers are adapting to change is to track the skills they request in job postings. Changes in these demands signal changes in what employers believe they need.
Based on SkyHive by Cornerstone data, UAE employers increasingly value workers who understand customers, can manage data, and who have strong character. Client interaction is first on the list of the fastest-growing skills in demand for 2023-24, followed by industry trend analysis and professional courage. Confidentiality and customer satisfaction also make the top 10.
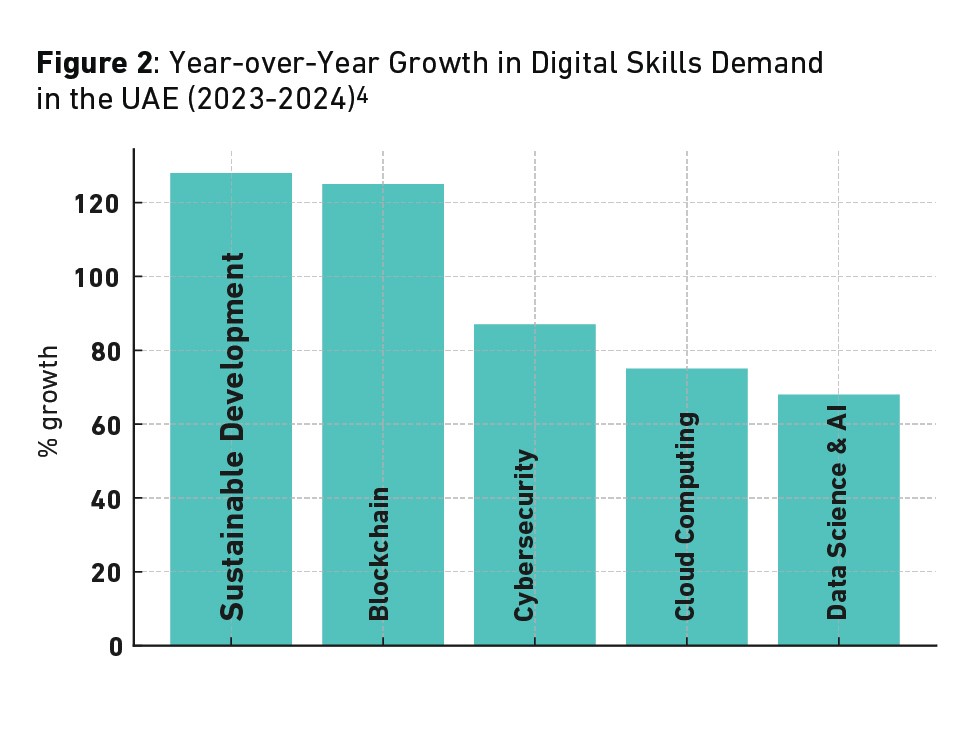
The drive for AI skills (and digital skills in general)
Over the past two years, demand for AI skills by UAE employers has soared. The overall numbers are still small, but not dissimilar to major players in the field. The UAE shows less demand for AI and machine learning skills than the United States or Japan, but more than the UK, Saudi Arabia, or Australia.
The other side of the equation is talent: the number of workers who actually have these skills. Some 4.1% of UAE workers listed AI skills on their profiles in 2023, comparable to the United States and ahead of other nations.
Green skills are also in demand, particularly in the UAE’s burgeoning construction industry. The fastest-growing green skills include environmental health and safety, quality inspection, and industry standard adherence.
Preparing Emirati youth for the workforce
The UAE has ambitious plans for its workforce, such as increasing the number of Emiratis in the workforce (Emiratization). The report concludes two strategies will be essential to achieving these goals:
- Equipping Arab youth with skills that complement AI
- Empowering Arab Youth to Showcase Essential Human Skills
Most AI experts argue that far more workers will work alongside AI than be replaced by it. The workers who are best able to incorporate AI tools to become more productive will have an edge, both in the UAE and around the world.
The crucial challenge for employers is to find out how to apply AI technology to their business problems. That is driving demand for a group of complementary technical, functional, and human skills designed to do just that. Job postings that call for AI skills also call for these skills, showing that employers believe these are critical to get the most out of AI tools.
Many of the complementary technical skills are specific to AI, like machine learning. But other skills have broader application, like data analysis, cloud computing, software integration, and Web3 development. Not only do these skills play a critical role in connecting AI applications to wider uses, they also provide young workers with a range of viable alternative pathways into careers.
The complementary functional skills include management, project management, training, marketing, and business strategy. These are the essential skills needed to identify where AI can best be used, build it into an organization’s business processes, and assess how well it is working.
There are complementary human skills as well: demonstrating responsibility, communication, collaboration, and problem solving. These human skills have always been valuable, but never more so than in times of rapid change. Employers globally are 2.5 times more likely to seek human skills than digital ones, and in the UAE, it’s three times as likely.
Despite the importance of human skills to employers, however, many workers fail to cite them on CVs or job profiles. Young workers are less likely to claim these skills than older ones. For example, 33% of global job postings call for the fundamental skill of communication. One in five (20%) of Gen X and Boomer workers claim this skill on their CVs, compared to 17% of Millennials and 12% of Gen Z.
There could be multiple factors at work in these gaps, including the possibility that many workers think human skills are either unimportant or too obvious to cite in a CV. Yet there is no question these skills matter to employers, and failure to claim them on a CV is a missed opportunity for those who have them.
Massar Al Ghurair: Building workforce connections for Emirati youth
AGF and SkyHive by Cornerstone are partners in Massar Al Ghurair, a web platform that speaks directly to meeting the UAE’s goals in the modern skills economy.
Massar Al Ghurair creates individualized journeys for Emirati and Arab youth aged 18-35, identifying learners' skills, assesses skill gaps in relation to job opportunities and careers, connects learners with relevant upskilling opportunities, and matches them with suitable job openings. By bringing together all the essential stakeholders, the Massar Al Ghurair model removes many of the inefficiencies in the traditional labor market.
Massar Al Ghurair aims to serve up to 45,000 learners, 50 employers, and 20 training providers, hosted on a secure cloud platform in the UAE. With this, the Abdulla Al Ghurair Foundation aims to significantly impact the Emirati talent pipeline, tapping into a motivated and growing segment of the local workforce, providing a steady stream of qualified candidates for organizations’ future needs, and fostering national economic growth and stability in line with the UAE National Vision.

